Google Tag Manager (GTM) is one of the most powerful tools for digital marketers, SEOs, and business owners who want to streamline tracking, enhance website analytics, and improve overall marketing performance. If you’ve ever felt frustrated with hard-coded tracking scripts or struggled to keep up with multiple tags, GTM is the solution you’ve been looking for. In this guide, we’ll break down how to use Google Tag Manager effectively and why it should be a foundational tool in your digital marketing stack.
What is Google Tag Manager?
Google Tag Manager is a free tool from Google that allows you to manage and deploy marketing tags (small pieces of code) on your website without needing to modify the site’s code directly. Instead of relying on a developer every time you need to update a tracking pixel or add a conversion tag, GTM provides a user-friendly interface that simplifies the process.
With GTM, you can:
- Track conversions from platforms like Google Ads and Facebook
- Implement advanced Google Analytics tracking without coding
- Set up event tracking for user interactions
- Manage scripts for remarketing and third-party tools
Why You Should Use Google Tag Manager
There are several key benefits to using GTM instead of manually embedding tracking codes on your website:
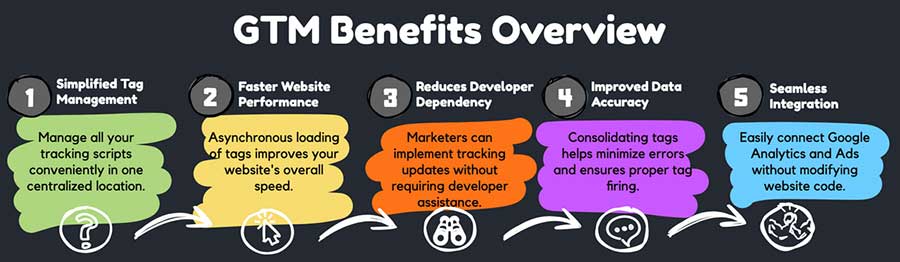
1. Simplified Tag Management
Managing multiple tracking scripts manually can get messy fast. GTM allows you to consolidate all your tags in one place, making updates and troubleshooting much easier.
2. Faster Website Performance
Every additional tracking script you manually add to a website can slow it down. GTM uses asynchronous loading, ensuring tags fire efficiently without negatively impacting page speed.
3. Reduces Developer Dependency
One of the biggest frustrations for marketers and SEOs is waiting on developers to implement tracking updates. With GTM, most tagging tasks can be handled within the platform, saving time and money.
4. Improved Data Accuracy
By managing all tracking codes in a single location, GTM helps reduce errors and ensures that tags fire correctly. You can also debug and test tags before pushing them live.
5. Seamless Integration with Google Analytics and Google Ads
If you’re running paid campaigns or tracking organic traffic, GTM makes it easy to set up conversion tracking, event tracking, and advanced analytics configurations without modifying website code.
How to Use Google Tag Manager
If you’re new to GTM, getting started may seem intimidating, but once you understand the basics, it becomes second nature. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
Step 1: Set Up a Google Tag Manager Account
- Go to Google Tag Manager
- Create an account and a container for your website
- Install the GTM code snippet in the
<head>and<body>sections of your site
Step 2: Understand Tags, Triggers, and Variables
- Tags: These are the pieces of code that send data to platforms like Google Analytics, Facebook Pixel, or LinkedIn Ads.
- Triggers: These define when and where a tag should fire (e.g., on a form submission or button click).
- Variables: These store dynamic values used in triggers and tags (e.g., tracking specific button clicks or URL paths).
Step 3: Set Up Google Analytics with GTM
- In GTM, create a new tag
- Choose Google Analytics: GA4 Configuration
- Enter your GA4 Measurement ID
- Set the trigger to “All Pages”
- Save and publish
Step 4: Track Events for Better Insights
One of the most powerful features of GTM is event tracking. You can track actions like form submissions, outbound link clicks, or scroll depth.
To track button clicks:
- Go to Triggers and create a new trigger
- Choose “Click – All Elements”
- Set it to fire when a button with a specific CSS class is clicked
- Attach this trigger to your tag
- Test and publish
Step 5: Test Your Setup with GTM’s Preview Mode
Before publishing any changes, use Preview Mode to ensure your tags fire correctly. This helps you catch errors before they affect live data.
Common Mistakes to Avoid with Google Tag Manager
Even experienced marketers can make mistakes when setting up GTM. Here are a few to watch out for:
- Not Testing Tags Before Publishing – Always use the built-in preview tool.
- Firing Too Many Tags on Page Load – This can slow down site speed and cause tracking conflicts.
- Incorrect Trigger Configurations – Make sure your tags fire at the right time and under the right conditions.
- Not Using Built-in Variables – GTM comes with many built-in variables that save time; enable them instead of creating custom ones.
Why Google Tag Manager is a Game-Changer for SEO
From an SEO perspective, GTM offers several advantages:
- It reduces code bloat, improving page speed and Core Web Vitals scores.
- You can track on-page interactions (like scroll depth and button clicks) to optimize user experience.
- It allows seamless A/B testing setups without modifying site code.
- It helps integrate advanced tracking solutions, like enhanced eCommerce tracking, to gain deeper insights into user behavior.
Final Thoughts: Make Google Tag Manager Work for You
If you’re still manually adding tracking scripts to your website, it’s time to switch to Google Tag Manager. Not only will it make your life easier, but it will also enhance your tracking capabilities, improve site performance, and give you better insights into how users interact with your site.
If you need help setting up GTM or optimizing your tracking strategy, let’s talk. Schedule a consultation to see how I can help you streamline your tracking and analytics.
Also, let’s connect on LinkedIn! Follow me here for more insights into digital marketing, SEO consulting, and Google Analytics Consulting.

